What is a Project?
A project is understood to be planning to consist of a set of interrelated and coordinated activities, with the express purpose of achieving specific results within the framework of the limitations imposed by prior conditioning factors: a budget, a time, or a series of recognized qualities.
It usually understands the preparation and arrangement in writing the theoretical, material, and human elements. It is needed to develop a unique product, service, or result. In certain areas, it can be equal to an outline, preceding script, first draft, etc.
The formal and theoretical features vary contingent on its nature and its object of study, and its parts. For example, some may highlight their bibliographic sources, while others will emphasize their methodology or impact upon the conclusion.
It is more likely to be fruitful when the leader (that is, who is in charge of it) establishes some control system. Or method through which all progress (or progress) monitor throughout the stages. drawbacks) of the project based on what plan. So that the necessary modifications can make in time to attain a better result and thus achieve all the objectives.
Types of Project
Projects can be classified according to their possibility of action, as follows:
Productive or private projects: Those whose ulterior drive is a success, that is, obtaining profit. They are usually present in the business, entrepreneurial or industrial field.
Public or social projects: Those are not for profit but have a significant impact on society or the population on a different scale: local, regional, even global. In general, they have as a promoter the State, the NGOs, or the corporate responsibility policies of the large transnational companies.
Community projects: Those committed to refining specific aspects of a given community, usually small, urban, and rural, satisfy their needs.
Life projects: It focuses on an individual’s life desires and their actual odds of achieving self-realization.
Research projects: Those whose impartial is the documentation or acquisition of sources and materials around a selected topic, as in Ad.
Steps of a Project
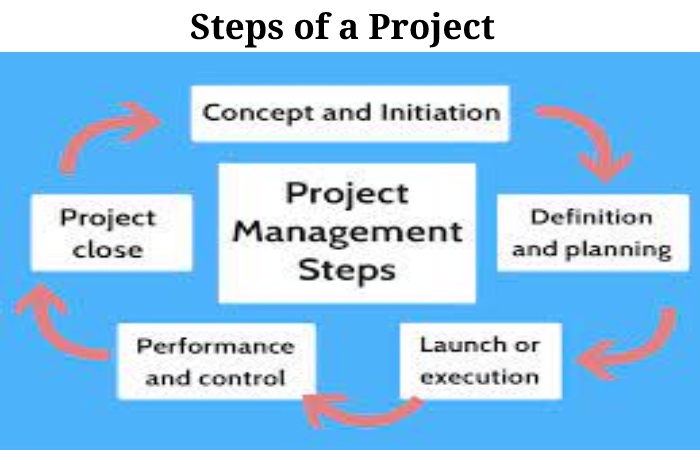
The project makes up of four stages:
Diagnosis: The essential and opportunity of the project are evaluated in its particular range of action to determine under what conditions it should happen and what stages it will involve, etc.
Design: The options, tactics, and plans that can lead to success discuss to meet the objective. The viability of the project, its relevance, and its specific wants to evaluate.
Execution: The implementation of what establishes in it.
Evaluation: The deductions of the project and the results obtained after its investigation review. It is a stage of switch and information based on improvement and accumulation of success factors over time.
Elements of a Project
The budget is the cost that the project application will have. It usually consists of the following elements:
Purpose and objectives: The section explains the problem that the project would solve, its aims, and the concrete, general, and specific goals.
Product or service: Here is a detailed account of the final product to be obtained, explaining how this would respond to what state in the objectives and its area of execution, that is, to other similar situations.
Schedule of activities: The steps to follow to meet the objectives are explained, arranged chronologically, and detailing the time their satisfaction would require.
Budget: The cost that the implementation of the project will have for its recipients and the detailed way the money will use in each phase of the project.
Expected results: A detailed description of the results that you want to obtain through the application of the project, often accompanied by your risk and profit margins.
Phases of a Project
Whatever the project, four phases always take place during its start-up. In many cases, they receive different names, but all of them bring together the same concept:
1. Initial Evaluation
Before developing and launching any project, the first thing to do is carry out an exhaustive analysis of the detected needs. And reflect on the origin, causes, and how to act.
2. Planning
Once the needs detect and the origin analyzed, it is time for planning, that is, to design the project. For this, it will be necessary to define the objectives to pursue. The phases through which they are going to pass, the duration of the project, the essential resources. The methods that are going to use, the monitoring that will carry out, the organization the work teams, costs, and financing. The communication strategies that will use or the indicators that will take into account for the evaluation.
3. Implementation of the Project
Once the planning does, the project can execute. It is time to carry out each of the established steps and carry out all the strategies and activities programmed. In this phase, continuous monitoring and evaluation are essential to ensure the project’s success. Since they allow the necessary improvements to make at all times.
4. Final Evaluation
Once the project finishes, the last phase will evaluate the results obtained. If the objectives initially set were achieved In addition, in this phase, the ideal is to analyze. Once it is clear what a project is, we can point out that, in the business world, project management is essential to achieve objectives as effectively as possible.
This management integrates all phases, from planning the project, the organization of both materials, financial and personal resources, implementation, and evaluation. In addition, it aims to guarantee the achievement of the proposed objectives within the established deadline, with the agreed budget and favouring a positive work environment.
Conclusion
A project is the planning and executing of a series of actions that aim to achieve a certain objective and carry out. So, a project is the idea of a certain task, for which we establish how it will carry out. In this way, must collect planning of the set of activities and carry them out.
Finally, must also include details of the set of resources and means necessary to carry it out. It can be of an infinite number of types. You should not always maintain a specific structure.