What is PMO?
PMO Meaning: A Project Management Office (PMO) is a group or department within a company, agency, or company that defines and maintains standards for project management within the organization.
The primary goal of a PMO is to take advantage of standardization and monitoring of project management processes, guidelines, and methods. For the office to be more effective, it must incorporate the culture and strategy of the organization.
And also, the popularity of the office has increased as more companies have achieved ROI with PMOs.
Nearly seven in ten companies worldwide have a PMO, a number that has remained constant for five years in a row, according to the Project Management Institute (PMI) Pulse of the Profession 2016 report.
Roles and Responsibilities of the PMO

A PMO is generally responsible for guidance, documentation, and metrics related to the practices surrounding project management and implementation within the organization. A PMO can also get involved in project-related tasks and track project activities through to completion. The office can report project activities, issues, and requirements to top management as a strategic tool to keep implementers. And also, decision-makers are on track towards business or mission-oriented goals and objectives.
A PMO generally bases its project management principles, practices, and processes on an industry-standard methodology. Here are some commonly used project management methods:
Agile: The agile method applies to projects requiring speed, flexibility, and continuous delivery of products to the customer in short delivery cycles.
Waterfall: The waterfall methodology allows for greater control at each stage of a project but can be very inflexible as the scope of the project changes.
Hustle: This term is based on the education of players in the game of rugby and is part of the Agile framework. Deliveries are due every 30 days. Workgroups that have had difficulty prioritizing work can improve productivity by switching to Scrum.
Six Sigma: Six Sigma is a methodology used to improve processes by eliminating defects or a product or service that does not meet specifications.
Types of PMO
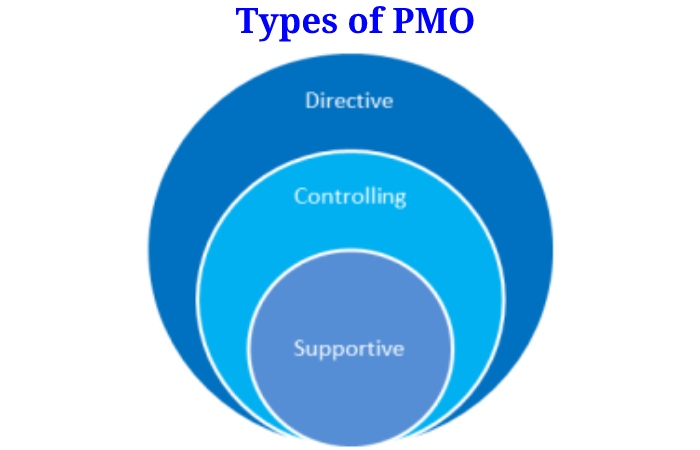
There is no such one-size-fits-all approach to PMO development; However, an effective PMO has a solid foundation that aligns with the company’s organizational strategy.
Designing and staffing a PMO for maximum effectiveness depends on various organizational factors. It including specific goals, traditional strengths, and cultural needs. The types of PMOs in organizations have not changed since 2010; Two-thirds of organizations have a department, regional, or divisional PMO or PMO. Three Basic Organizational Structures for a Project Management Office:
The Project Repository: This model is most common in organizations that enable distributed, business-oriented project ownership or in companies with poor central governance. The project office only serves to provide information about the methodology and standards of the project. Project managers continue to report and fund by their respective business units.
The project consultant model: The model assumes a willingness to share some project management practices between business functions and uses the project office to coordinate communication. Best practices document and share. Also, project performance actively monitor. The PMO in this model is a fixed personnel structure and has specific supervisory responsibility for all projects.
The Enterprise Project Management Office (EPMO): This model also assumes a governance process that involves the PMO in all projects, regardless of their size, to assess the scope; Assign resources; and review time, budget, risk, and impact assumptions before running the project. Funding is usually a combination of a direct budget allocation for essential services and a service fee for others.
How PMOs can be Effective?
PMOs exist in around half of the organizations, according to the PMI report. While they play a critical role in creating business value, many companies still struggle to define the role of EPMO, position it for long-term success. And use the office to achieve strategic goals.
Effective PMOs have broad company-wide responsibilities and help drive strategy and focus on creating value.
According to the PMI report, about 27% more projects complete successfully. And also, there are 42% fewer projects with a fluid scope when companies align their EPMO with strategy.
Conclusion
A PMO can also get involved in project-related tasks and track project activities through to completion. The office can report project activities, issues, and requirements to top management as a strategic tool.


