Work Breakdown Structure(WBS) Definition
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a hierarchical deliverable-driven work breakdown that the project team will execute to meet project goals and create required deliverables. A WBS is the cornerstone of real project planning, execution, control, monitoring, and also reporting. All work contained in the SRT must be identified, estimated, scheduled, and also budgeted.
Diagram of Work Breakdown Structure(WBS)

The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) develop to establish a common understanding of the project’s scope. It is a hierarchical account of the work that must do to complete the deliverables of a project. Each level downstream of the WBS represents an increasingly full description of the project deliverables.
The first two heights of the WBS (the root node and level 2) define a set of thoughtful outcomes that collectively and wholly represent 100% of the project’s scope. At each following story, the children of a parent node together and exclusively signify 100% of the content of its parent node.
Quality of the Decomposition Work Breakdown Structure(WBS)
A well-designed WBS describes planned results rather than planned actions. Results are the desired ends of the project, such as a product, outcome, or service, and can predict with precision. Inventories, on the other hand, can be problematic to predict accurately. A well-designed WBS makes it easy to allocate WBS elements to any project activity. A good WBS should have the following characteristics:
Definable: It can be easily described and understood by project participants.
Manageable: A meaningful unit of work in which specific responsibilities and powers can assign to a responsible person.
Estimable: And also, the duration can be estimated when needed to complete, and the cost can calculate in the resources required to complete.
Independent: interface or minimal dependence on other elements in progress (i.e., assignable to a single control account and distinguishable from other work packages).
Integrated: Integrates with other project work items and higher-level cost estimates and schedules to include the entire project.
Measurable: And also, it can measure progress; It has a start and end dates and quantifiable milestones.
Adaptable: Flexible enough that adding/removing scope of work can be easily integrated into the WBS framework.
Guidelines for Developing the Work Breakdown Structure(WBS)
Developing the work breakdown structure involves breaking down the main activities or sub-activities of the project into smaller, more manageable activities until the exercises are defined in sufficient detail to support the management and development of the project’s work. The lowest level items in a branch are called work packages. Here are some tips for developing a work breakdown structure(WBS) that can effectively express tasks:
- Always express work breakdown structure doings at the lowest granularity levels in verbal form.
- Review the work breakdown structure(WBS). Ensure that all deliverables fully covers by the tasks defined in the work breakdown structure(WBS).
- Make sure that testing and training take into account.
- Ensure that non-IT work packages also include, such as documentation and review activities included in the framework.
- Make sure that other support activities such as product/service launch and implementation activities plan.
- Make sure that version approval cycles take into account.
- And also include the project management deliverables in the project (for example, the production of the project plan). Include all deliverables to be completed or delivered by the customer or any outside party.
- And also, check the work breakdown structure in contradiction of the project objective specified in the project charter for all activities that need to include in the work breakdown structure(WBS).
Use Cases for the Work Breakdown Structure(WBS)
Typical use of the breakdown structure as a project management tool includes the work breakdown structure (WBS), the resource breakdown structure, the risk breakdown structure, the work breakdown structure, the organization ( OBS), or sometimes referred to as an organization chart.
1. Resource Allocation Structure
The Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) is a project management tool that provides a hierarchical breakdown of resources, either structured by resource category, types, or by IT / business function with resource requirements.
2. Risk Allocation Structure
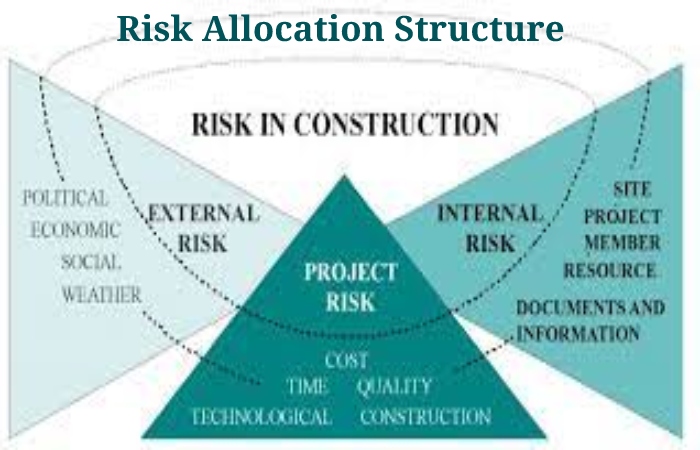
Risks are everything in any IT project. The existence of a risk harms the schedule, costs, and quality of the project. In project management, the project manager is responsible for managing risk and ensuring that the project will deliver on time, within the project’s scope, and to the standard of the expected user. One of the most popular risk management tools is the risk allocation structure.
Risk allocation Structure is the hierarchical breakdown of risks, starting with the root node element representing the project and working down to the different risk categories, then finer-level chances.
In addition to presenting the project risks in a risk allocation structure, it is possible to combine the color legend to represent the impact of the risk. And also, take an appearance at the Risk Breakdown Structure example underneath. An impact legend is set up with five items, representing the five levels of impact that risks can have on the project with five different color codes.
3. Breakdown Organizational Structure
The organization breakdown structure sometimes refers to as an organization chart, a project management tool widely used to represent the project organization. And also, it usually starts with the project sponsor, and all key stakeholders included. When presenting the organizational structure, consider the organization or group requesting the project and its patronage and authority level.
What are the Levels of a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)?
A WBS in project management supports large and complex projects and divides the project’s scope into more manageable parts to facilitate planning, planning, and delivery. Project task and deliverable levels create to support project planning, execution, Marketing campaign planning, and monitoring. There are four main stages of a WBS, described below:
The upper level: the title of the project or the final delivery.
Control account: The main phases and deliverables of the project.
Work Packages: The group of tasks that lead to the controlling account level.
Activities: the tasks required to complete the work package.
These levels find in all the different types of work breakdown structures.
What are the Types of Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)?
There are two main types of WBS: delivery-based and phase-based. A deliverable-based WBS identifies the deliverables and scope of the project. At the same time, the phase-based WBS shows the final delivery at the top, and the lower level offers the five phases of a project (initiation, planning, execution, control, and closing).
There are also insufficient rare types of work breakdown structures:
- A verb-oriented WBS defines deliverables in terms of actions.
- A name-oriented WBS defines work in terms of components (this also call a product breakdown structure).
- And also, phased WBS divides the project into phases for long-term projects.
A work breakdown structure is a very flexible tool. It can take the form of a simple numbered list (also known as an overview), a basic tree chart, or smooth a Gantt chart. When a Gantt chart is share as a greater project management tool, the WBS can shift to planning, assigning, tracking, and tracking your team’s progress.
Conclusion
A work breakdown structure (WBS) is a graphic, hierarchical, delivery-oriented deconstruction of a project. It is a useful diagram for project managers because it allows them to step back from the result of a project and identify all the activities necessary for the success of a project.
All stages of a project outline in the flowchart of a work breakdown structure, making it an essential project management tool for planning and scheduling. The final product base on the diagram and the below subdivide levels indicate the phases, final products. And tasks required to complete the project.