SaaS Sales Definition
SaaS sales are the process of selling web-based software to clients. Salespeople focus on acquiring new customers and upselling or retaining current clients.
It is supported, maintained, and engineered by an external company. The price usually high requires a longer sales cycle and more touchpoints from Sales and Marketing before the customer is ready to buy.
Marketing nurtures each lead until they are “sales qualified.” Then, a salesperson follows up with the prospect to gauge the next steps.
Just because a lead is sales qualified doesn’t mean they’re ready to buy — or ready for a demo.
SaaS salespeople must communicate the benefits and features of their software.
Reps also must well-versed in how the software works to demonstrate and troubleshoot the product during presentations.
What is SaaS?

Remember the days of unwrapping CD-ROMs, uploading them to your computer, and having access to that software from your computer? Those days are gone. SaaS hosted, secured, and updated by an outside vendor.
It means SaaS often yields lower entry costs than traditional software, easier upgrades, and better integrations.
What are Saas Sales Commission?
SaaS commission, like other sales verticals, paid when a rep closes new business or renews existing accounts.
- It award based on monthly recurring revenue (MRR) or annual contract value (ACV).
- And also, Some organizations wait for new clients to submit payment before awarding commission.
- This model meant to avoid paying a commission on a customer that churns quickly or reneges on their agreement.
- The accelerator model of commission means every dollar a rep brings in over goal, their commission rate increases by a percentage point
What are Saas Sales Models?
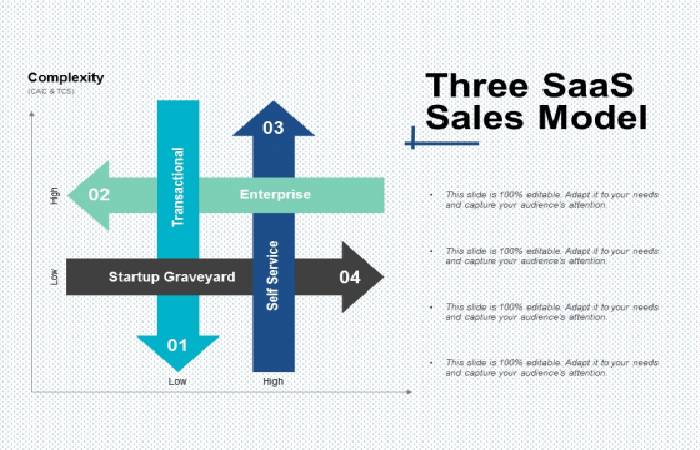
The proper sales model indicates how many salespeople you should hire, how you’ll interact with your customers, who they are, and how
you’ll close their business.
And also, It’s crucial to choose the right model and know when your organization needs to evolve. Here are the three most common SaaS sales models.
1. Customer self-service:
This model works best when selling lower-priced SaaS at a high volume (i.e., Spotify subscriptions, a Medium
membership, or a phone plan).
2. Transactional sales:
Transactional selling is the most common and the most scalable of the three models. This software typically sold to small and medium businesses over the phone and occasionally in person.
3. Enterprise sales:
This model reserved for software sold at low volume and high price. These solutions often full-scale, highly specialized, or cutting edge.


